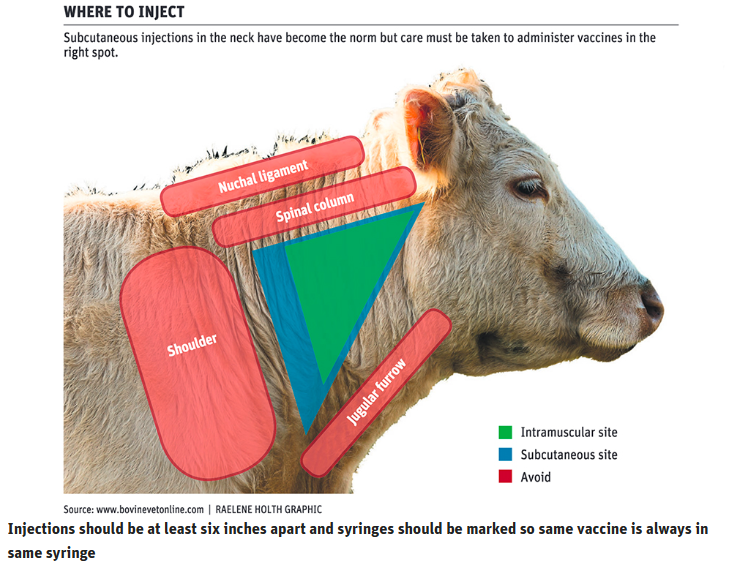
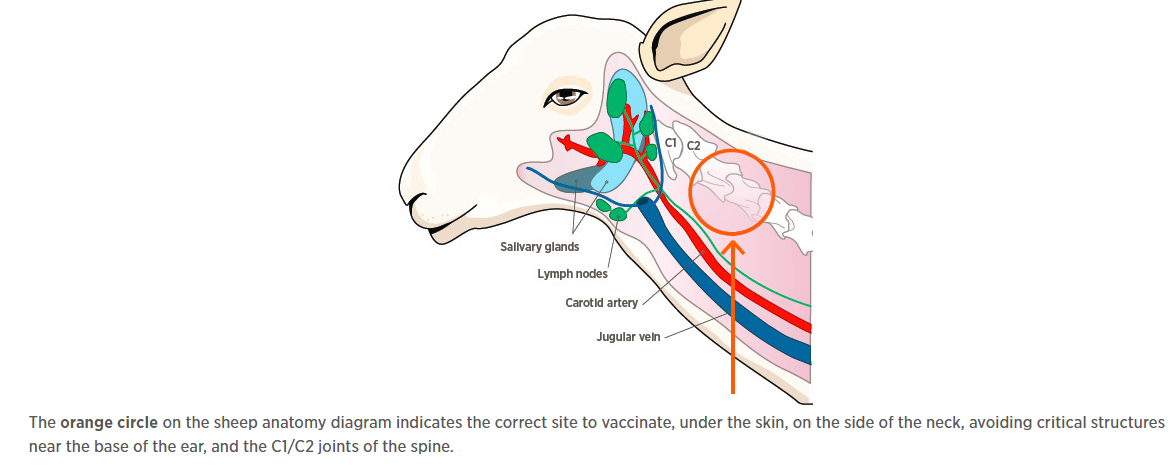
Keeping Livestock Vaccinations Up to Date
Protecting Your Business Like Insurance
In livestock production, risk management is everything. Whether you manage cattle, sheep, goats, or horses, your animals are one of your most valuable business assets. Just like you insure your property, vehicles, and equipment, vaccinations act as biological insurance for your herd.
A proactive vaccination program protects animal health, improves productivity, safeguards market access, and reduces the risk of costly disease outbreaks. The principle is simple: invest a little now to avoid significant losses later.
Vaccinations Are Business Insurance
When you pay an insurance premium, you’re covering yourself against an event that might happen. Vaccinations follow the same logic — they’re a preventive measure to avoid financial and production losses:
Insurance compensates you after a loss occurs.
Vaccinations stop the problem before it starts.
Skipping vaccinations is like cancelling your insurance policy — it exposes your livestock, your business, and your livelihood to unnecessary risk.
Understanding Clostridial Diseases
One of the biggest threats to livestock enterprises in Australia is clostridial disease. These conditions are caused by Clostridium bacteria, which are common in soil, water, and even the digestive system of healthy animals.
Key facts about clostridial diseases:
Spore-forming and long-lasting - Bacteria can survive in the environment for years.
Sudden onset - Death can occur within hours, often with no warning.
Difficult to treat - Once toxins spread, treatment is rarely successful.
Easily preventable - Vaccination is highly effective and low cost.
This is why 5-in-1 and 7-in-1 vaccines are standard for most cattle and sheep operations across Australia.
Recommended Livestock Vaccinations
Cattle
Cattle require protection against diseases that impact productivity, reproduction, and animal welfare:
5-in-1 or 7-in-1 Vaccine – Protects against key clostridial diseases:
Blackleg (Cl. chauvoei)
Pulpy Kidney / Enterotoxaemia (Cl. perfringens Type D)
Tetanus (Cl. tetani)
Black Disease (Cl. novyi Type B)
Malignant Oedema (Cl. septicum)
Botulism – Critical in northern Australia where phosphorus-deficient soils increase susceptibility.
Pestivirus (BVDV) – Reduces reproductive losses and calf disease.
Bovine Ephemeral Fever (Three-Day Sickness) – Protects against sudden production drops during outbreaks, especially in bulls.
Tick Fever (endemic regions) – Protects against blood-borne parasites transmitted by cattle ticks.
Leptospirosis (Lepto) – Prevents abortions, reduced fertility, and illness in cattle. Importantly, Lepto is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can infect humans. Vaccination is essential for both business protection and workplace safety.
Sheep
Sheep are highly vulnerable to sudden disease outbreaks, especially during high-growth periods:
5-in-1 Vaccine – Protects against clostridial diseases including pulpy kidney, tetanus, black disease, malignant oedema, and blackleg.
6-in-1 Vaccine – Includes protection against Cheesy Gland (CLA), a disease causing carcass downgrades and wool quality issues.
Erysipelas Arthritis Vaccine – Recommended for lambs in high-risk marking conditions.
Ovine Johne’s Disease (OJD) – Used in affected regions to reduce long-term losses.
Footrot Vaccines (where required) – Controls severe outbreaks in high-rainfall environments.
Goats
Goats share many of the same disease risks as sheep but need programs tailored to enterprise goals:
5-in-1 or 6-in-1 Vaccine – Protects against clostridial diseases.
Caseous Lymphadenitis (CLA) – Prevents abscesses and carcass downgrades.
Johne’s Disease Vaccine – Useful in high-risk areas.
Leptospirosis (Lepto) – Recommended where dairy production or close human handling occurs.
Horses
Horses require regular vaccination to protect against life-threatening and highly contagious diseases:
Tetanus – Often included in a combined 2-in-1 vaccine with strangles.
Strangles – Prevents highly infectious respiratory illness.
Hendra Virus (northern Australia) – Protects horses and humans from a deadly disease.
Equine Influenza (where required) – Recommended for performance and racing horses.
The Business Case
A well-managed vaccination program protects more than animal health — it protects your bottom line.
A $5–$10 per head vaccine can prevent hundreds of dollars in treatment costs and production losses.
Diseases like Leptospirosis carry serious human health risks, making vaccination a key part of workplace safety.
Maintaining herd immunity safeguards animal welfare, business continuity, and ongoing market access.
Vaccination is one of the most cost-effective risk management strategies available to livestock producers.
Key Takeaways
Vaccinations are a form of business insurance — small costs now prevent major losses later.
Clostridial diseases are sudden, deadly, and almost impossible to treat — prevention is the only reliable option.
Leptospirosis vaccination protects both livestock productivity and human health.
Tailor your vaccination program to your region, enterprise type, and market requirements in consultation with your vet.
Kind Regards,
Matt Brown
Livestock & Business Development Specialist
Useful Links
Information:
https://www2.zoetis.com.au/livestock-solutions/northern-beef/
https://www2.zoetis.com.au/livestock-solutions/southern-beef/
https://www2.zoetis.com.au/livestock-solutions/sheep/
https://www.mla.com.au/globalassets/mla-corporate/research-and-development/program-areas/animal-health-welfare-and-biosecurity/210517-vaccination-for-beef-cattle-in-southern-australia.pdf
https://www.mla.com.au/contentassets/e196543ebe564287b54de6993fafd518/mla-vaccination-for-beef-cattle-in-northern-australia-0922-web.pdf
https://www.mla.com.au/globalassets/mla-corporate/research-and-development/program-areas/animal-health-welfare-and-biosecurity/210517-vaccination-in-sheep-flocks.pdfResources and Tools:
https://www2.zoetis.com.au/livestock-solutions/farmplanner
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is true and correct to the best of my knowledge at the time of publication. It is intended for general guidance and informational purposes only. Readers are encouraged to verify any information and seek independent advice relevant to their individual circumstances, particularly where legal, financial, or regulatory compliance matters are concerned.